What Is SEO and why do you need it? An explanation for beginners
Take a moment and think about the last time you wanted to learn or buy something online. If your first instinct is to head to Google, you're in good company: 80% of searchers prefer it. How often do you click an advertisement or head beyond the first page of results? As the first page of search results earns over 95% of clicks, it's a smart idea to make sure your site appears in those results when your customers are looking.
What is SEO?
SEO stands for search engine optimization, which is a set of practices designed to improve the appearance and positioning of web pages in organic search results. Because organic search is the most prominent way for people to discover and access online content, a good SEO strategy is essential for improving the quality and quantity of traffic to your website.
Why is SEO important?
To understand the value of SEO, let's break our definition into three parts:
Organic search results: the unpaid listings on a search engine results page (SERP) that the search engine has determined are most relevant to the user’s query. Ads (in this context, PPC or pay-per-click ads) make up a significant portion of many SERPs. Organic search results are distinct from these ads in that they are positioned based on the search engine’s organic ranking algorithms rather than advertiser bids. You can’t pay for your page to rank higher in organic search results.
Quality of organic traffic: how relevant the user and their search query are to the content that exists on your website. You can attract all the visitors in the world, but if they're coming to your site because Google tells them you're a resource for Apple computers when you're a farmer selling apples, those visitors are likely to leave your site without completing any conversions. High-quality traffic includes only visitors who are genuinely interested in the products, information, or other resources your site offers. High-quality SEO capitalizes on the search engine’s effort to match a user’s search intent to the web pages listed in the SERP.
Quantity of organic traffic: the number of users who reach your site via organic search results. Users are far more likely to click on search results that appear near the top of the SERP, which is why it’s important to use your SEO strategy to rank relevant pages as high as you can. The more high-quality visitors you attract to your site, the more likely you are to see an increase in valuable conversions.
How does SEO work?
Search engines like Google and Bing use crawlers, sometimes also called bots or spiders, to gather information about all the content they can find on the internet. The crawler starts from a known web page and follows internal links to pages within that site as well as external links to pages on other sites. The content on those pages, plus the context of the links it followed, helps the crawler understand what each page is about and how it’s semantically connected to all of the other pages within the search engine’s massive database, called an index.
When a user types or speaks a query into the search box, the search engine uses complex algorithms to pull out what it believes to be the most accurate and useful list of results for that query. These organic results can include web pages full of text, news articles, images, videos, local business listings, and other more niche types of content.
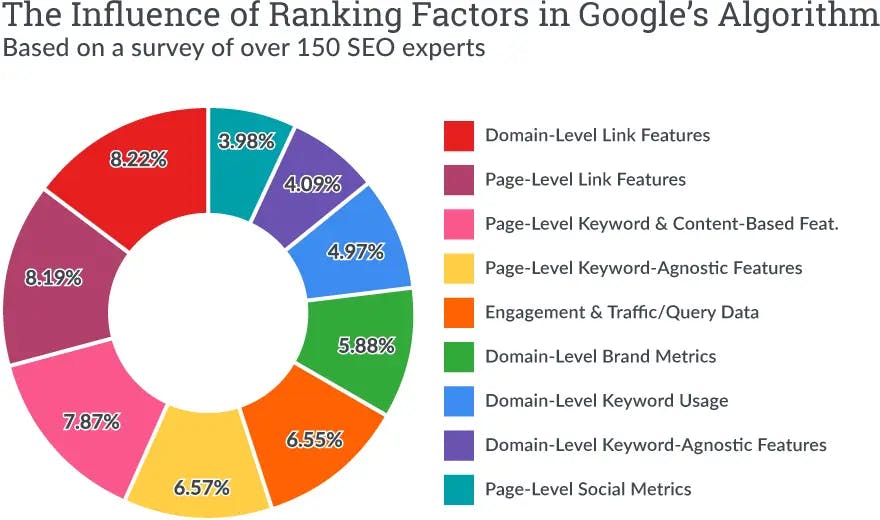
There are a lot of factors that go into the search engines’ algorithms, and those factors are evolving all the time to keep up with changing user behavior and advances in machine learning. Here's how a group of experts ranked their importance.
Ranking Factors
Many factors determine the ranking of a particular page, including:
- Keyword density, or the frequency with which a targeted word or phrase appears in the content of the page. SEO is improved by keywords that are used appropriately.
- Bounce rate, or how often a user visits the page and exits without visiting any other pages. A high bounce rate can detract from page ranking.
- Metadata, or the information that summarizes the content on the page.
- Social media traffic, indirectly signals that a page contains content that’s in high demand. High traffic from social media is beneficial to SEO, but a lack of social media traffic doesn’t necessarily have a negative impact.
- Links, including backlinks, outbound links, and internal links, indicate credibility and relevance to and from other content on the internet. Google looks favorably on sites that strategically direct traffic to other sources.
- EAT Google’s acronym for expertise, authority, and trustworthiness), which signifies that a page has a reputable author.
- Security is signified by a site’s SSL certificate, which search engines use to verify that site has a secure connection and it’s safe to share personal information.
- Load speed, or the time it takes a web page to completely load.
- Mobile responsiveness, or how a web page adjusts to different screen sizes.
- User experience, or the features that could improve (or diminish) a user’s interaction with the content on a page.
SEOs use their understanding of these ranking factors to develop and implement search marketing strategies that include a balance of on-page, off-page, and technical best practices. An organization that hopes to earn and maintain high SERP rankings and, as a result, lots of high-quality user traffic, should employ a strategy that prioritizes user experience, employs non-manipulative ranking tactics, and evolves alongside search engines’ and users’ changing behaviors.
It should be noted that while other digital marketing practices like conversion rate optimization (CRO), pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, social media management, email marketing, and community management are often closely related to SEO, these other tactics are generally outside the scope and definition of traditional search marketing. If you’re interested in learning more about any of these areas, the Moz Blog includes categories related to all of these topics and others, too.
On-page and off-page SEO
On-page or on-site SEO refers to the practice of optimizing web page content for search engines and users. On-page SEO focuses more specifically on what the site or web page is about.
The most common on-page practices include optimizing title tags, headings, URL structure, image alt text, page content, schema markup, social tags, and page experience.
Off-page SEO is related to the methods and strategies performed outside of your website to impact your rankings within the search engine results pages. Off-page SEO also affects search engine scenarios, such as higher ranking on search engines and page authority.
Off-Page SEO often involves gathering links from other websites that point back to your site, also known as backlinks. Using backlinks with off-page SEO includes the number of referring domains, the authority of links, do follow versus Nofollow linking, anchor text, and relevance of the content linked. Off-page SEO can also include brand mentions and testimonials as well.
White HAT vs. Black HAT SEO
White hat and black hat SEO are specific techniques used to drive traffic to websites. White hat or ethical techniques are used to drive more traffic to websites, optimize content for the long term, and give the site visitors more content related to their interests.
Some white hat practices include providing quality and relevant content, including well-captioned images, relevant links, clean HTML, and unique relevant titles and tags.
In contrast, black hat techniques provide short-term solutions to trick a search engine’s algorithms into ranking a site or page higher by treating it is as unique content. Some black hat methods that are used include creating duplicate content, using invisible or stuffed keywords, cloaking or redirecting users, and using irrelevant links for the sole purpose of ranking higher on search engines.
###How does SEO support my marketing efforts? SEO works to increase your site traffic and brand authority by inviting highly interested visitors to explore your pages. Generally speaking, depending on the business goals you're chasing and the customer intent you're targeting, those interested visitors are more likely to convert by making a purchase or becoming a lead. Beyond reaching people who are ready to purchase, practicing good SEO will help searchers unaware of your brand prepare to become customers in the future. It's an incredibly powerful tool in that it can target people at any stage of the marketing funnel.
SEO is unique.
Traditional marketing is focused on outbound messaging. You craft a message, distribute it to likely targets, and hope the people seeing your advertisement are in the right frame of mind to make a purchase.
Digital ads do the same thing as traditional print ads—they're just online.
Conclusion
SEO is the practice of optimizing websites to make them reach a high position in Google’s – or another search engine’s – search results.
Don’t use any black-hat SEO tricks, because eventually, this will have negative consequences for your rankings. Instead, practice sustainable SEO, with your user in mind, and you will benefit in the long run.